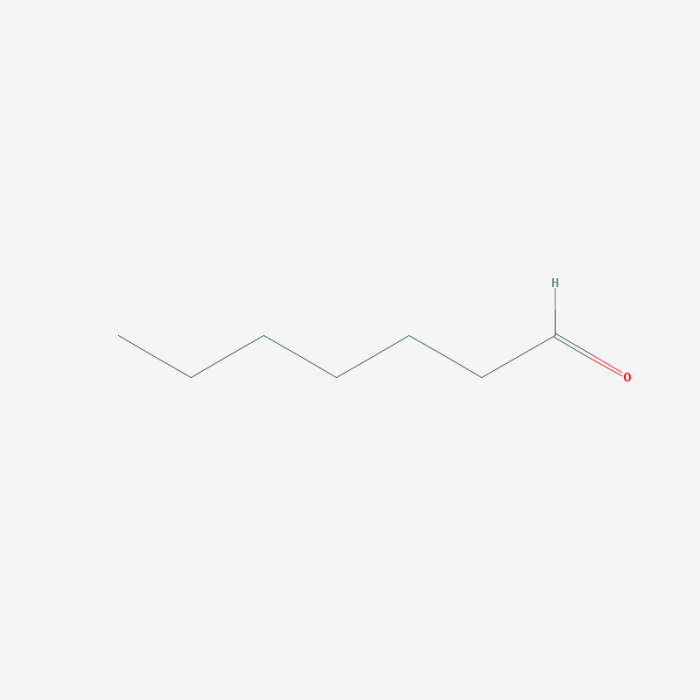
Name the aldehyde displayed below. – In the realm of organic chemistry, aldehydes stand out as versatile and reactive compounds. Understanding their nomenclature is crucial for effective communication and scientific exploration. This comprehensive guide delves into the IUPAC rules and common practices for naming aldehydes, empowering readers with the knowledge to accurately identify and describe these essential molecules.
Aldehydes, characterized by their carbonyl group and alkyl or aryl substituents, play diverse roles in various chemical processes. Their naming conventions follow a systematic approach, ensuring clarity and consistency in scientific discourse.
Introduction
Aldehydes are organic compounds characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to a hydrogen atom and an alkyl or aryl group. They are highly reactive and versatile functional groups, playing crucial roles in various chemical reactions and biological processes.
Correctly naming aldehydes according to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) rules is essential for effective scientific communication and unambiguous identification of these compounds.
Structural Features of the Aldehyde
The structural features of an aldehyde include:
- Carbonyl Group:The carbonyl group (C=O) is the defining characteristic of an aldehyde. It consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom.
- Alkyl or Aryl Group:Aldehydes contain an alkyl or aryl group attached to the carbonyl carbon atom. Alkyl groups are aliphatic hydrocarbon chains, while aryl groups are aromatic hydrocarbon rings.
Based on the alkyl or aryl group, aldehydes can be classified into different types:
- Aliphatic Aldehydes:Aldehydes with alkyl groups attached to the carbonyl carbon atom.
- Aromatic Aldehydes:Aldehydes with aryl groups attached to the carbonyl carbon atom.
- Heteroaromatic Aldehydes:Aldehydes with heteroaryl groups (aryl groups containing heteroatoms) attached to the carbonyl carbon atom.
IUPAC Nomenclature Rules for Aldehydes, Name the aldehyde displayed below.
The IUPAC nomenclature rules for aldehydes follow a systematic approach:
- Parent Chain:Identify the longest carbon chain containing the carbonyl group. This chain determines the base name of the aldehyde.
- Prefix:Use prefixes to indicate the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain. For aldehydes, the prefix “al” is used.
- Suffix:The suffix “-al” is added to the end of the base name to indicate the presence of the aldehyde functional group.
Example:Butanal (CH 3CH 2CH 2CHO):
- Parent Chain: Butane (4 carbon atoms)
- Prefix: But-
- Suffix: -al
Common Nomenclature for Aldehydes
In addition to IUPAC names, aldehydes also have common names based on their source or the functional group present in the molecule. Some common names for aldehydes include:
- Formaldehyde:Methanal (HCHO)
- Acetaldehyde:Ethanal (CH 3CHO)
- Benzaldehyde:Benzenecarboxaldehyde (C 6H 5CHO)
- Vanillin:4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde (C 8H 8O 3)
Additional Naming Considerations
When naming aldehydes, additional considerations may arise:
- Multiple Functional Groups:If an aldehyde contains multiple functional groups, the aldehyde group takes precedence in naming.
- Complex Substituents:Complex substituents on the alkyl or aryl group may require specific prefixes or suffixes in the name.
Example:
-Bromo-3-methylbutanal (CH3CHBrCH(CH 3)CHO):
- Parent Chain: Butane (4 carbon atoms)
- Prefix: But-
- Suffix: -al
- Substituents: 2-Bromo (Br) and 3-Methyl (CH 3)
Frequently Asked Questions: Name The Aldehyde Displayed Below.
What is the significance of naming aldehydes correctly?
Correct aldehyde nomenclature is essential for precise communication in scientific research, ensuring unambiguous identification and understanding of molecular structures.
How do IUPAC rules guide aldehyde naming?
IUPAC rules provide a standardized framework for naming aldehydes, assigning systematic names based on the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain and the presence of functional groups.
What are common considerations for naming aldehydes with complex structures?
When naming aldehydes with complex substituents or multiple functional groups, additional rules apply to ensure clarity and accuracy in their identification.