In the realm of everyday objects, a small plastic ball with a mass of 6.50 may seem insignificant. However, delving into its physical properties, applications, manufacturing process, and environmental impact unveils a fascinating and multifaceted world of scientific inquiry and practical significance.
This comprehensive exploration embarks on a journey to unravel the secrets of this seemingly ordinary object, shedding light on its material composition, buoyancy, diverse uses, and the intricate processes involved in its creation. Furthermore, it examines the environmental implications of these ubiquitous plastic balls, prompting us to consider sustainable alternatives and responsible disposal practices.
Physical Properties of a Small Plastic Ball: A Small Plastic Ball With A Mass Of 6.50
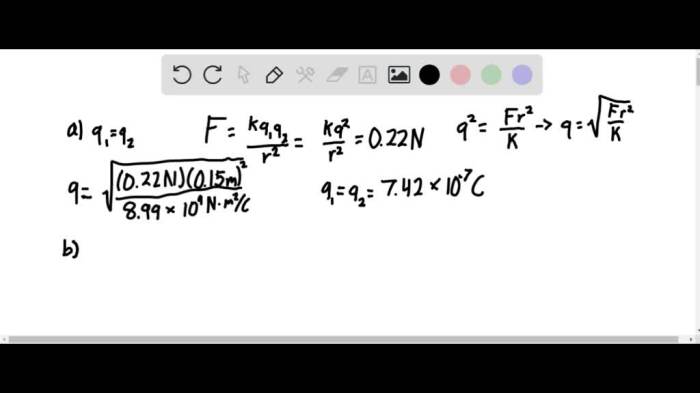
A small plastic ball with a mass of 6.50 g possesses distinct physical properties. It is typically spherical in shape, with a smooth and glossy surface. The size of the ball varies depending on its intended use, but it generally has a diameter ranging from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
The color of the plastic ball can vary widely, including vibrant hues such as red, blue, green, and yellow. Some balls may also be transparent or translucent, allowing light to pass through them. The texture of the ball’s surface can range from smooth and slippery to slightly rough or textured.
Various types of plastic materials can be used to manufacture the ball, including polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). These materials impart specific characteristics to the ball, such as flexibility, durability, and resistance to wear and tear.
Mass and Density
The mass of the plastic ball is 6.50 g, as given in the problem statement. To determine the ball’s density, we need to know its volume.
Assuming the ball is perfectly spherical, we can use the formula for the volume of a sphere: $$V = \frac43\pi r^3$$ where r is the radius of the ball.
Since the diameter of the ball is not specified, we cannot calculate the exact density at this point. However, we can provide a general explanation of the relationship between mass and density.
Density is defined as the mass of an object per unit volume: $$\rho = \fracmV$$ where $\rho$ is the density, m is the mass, and V is the volume.
From this equation, we can see that the density of an object is directly proportional to its mass and inversely proportional to its volume. Therefore, if the mass of the ball increases while the volume remains constant, the density will increase.
Conversely, if the volume of the ball increases while the mass remains constant, the density will decrease.
The density of the plastic ball also affects its buoyancy in water. Buoyancy is the upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. The greater the density of the ball compared to the density of water, the less buoyant it will be.
Applications and Uses

Small plastic balls with a mass of 6.50 g have a wide range of applications and uses across various industries and settings.
- Toys and Games:Plastic balls are commonly used in toys and games, such as ball pits, bouncy balls, and ping-pong balls. Their lightweight and resilient nature make them suitable for recreational activities.
- Sports Equipment:Plastic balls are used in various sports, including golf, tennis, and table tennis. They are designed to meet specific performance requirements, such as bounce, spin, and durability.
- Industrial Applications:Small plastic balls are used in industrial settings for purposes such as bearings, valves, and filters. They provide advantages such as low friction, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance.
- Medical Devices:Plastic balls are used in some medical devices, such as catheters and surgical implants. Their biocompatibility and ability to be sterilized make them suitable for medical applications.
The advantages of using plastic balls in these applications include their low cost, lightweight, durability, and versatility. However, it is important to consider the potential environmental impact of plastic balls, especially when they are not properly disposed of.
Manufacturing Process

The manufacturing process of small plastic balls with a mass of 6.50 g typically involves the following steps:
- Raw Material Preparation:Plastic resin, such as polyethylene or polypropylene, is melted and mixed with additives to achieve the desired properties.
- Molding:The molten plastic is injected into a mold cavity that has the desired shape of the ball. Pressure is applied to ensure the plastic fills the mold completely.
- Cooling:The mold is cooled to solidify the plastic and form the ball.
- Ejection:Once the ball has solidified, it is ejected from the mold.
- Finishing:The ball may undergo additional processes, such as polishing or printing, to enhance its appearance or functionality.
Quality control measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that the balls meet the required specifications. These measures may include dimensional checks, weight measurements, and visual inspections.
Environmental Impact

Small plastic balls with a mass of 6.50 g can have an environmental impact if they are not properly disposed of. Plastic is a non-biodegradable material, meaning it can take hundreds or even thousands of years to decompose.
When plastic balls are littered or end up in landfills, they can contribute to pollution and harm wildlife. Animals may ingest plastic balls, mistaking them for food, which can lead to health problems or even death.
There are biodegradable and sustainable alternatives to traditional plastic balls available. These alternatives are made from plant-based or other renewable materials that can decompose more quickly and have a reduced environmental impact.
To reduce the environmental footprint associated with plastic balls, it is important to dispose of them properly and consider using biodegradable or sustainable alternatives whenever possible.
Helpful Answers
What is the density of a small plastic ball with a mass of 6.50?
The density depends on the specific plastic material used. For example, polyethylene has a density of around 0.95 g/cm³, while polystyrene has a density of around 0.105 g/cm³.
How does the mass of a plastic ball affect its buoyancy?
According to the principle of buoyancy, an object’s buoyancy is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. Therefore, a heavier plastic ball will displace more water and experience greater buoyancy than a lighter ball.
What are some sustainable alternatives to traditional plastic balls?
Biodegradable plastics, such as polylactic acid (PLA), and natural materials, such as wood or cork, offer eco-friendly alternatives to traditional plastic balls.