The WJ IV Achievement Clusters and Subtests, an esteemed assessment tool, provide invaluable insights into students’ academic performance. By delving into the intricacies of these clusters and subtests, educators and professionals gain a comprehensive understanding of an individual’s cognitive abilities and academic skills.
This comprehensive analysis empowers educators to identify areas of strength and weakness, pinpoint specific learning needs, and tailor educational interventions to maximize each student’s potential.
1. WJ IV Achievement Clusters and Subtests Overview
The WJ IV Achievement Clusters and Subtests are a comprehensive assessment tool designed to evaluate a student’s academic achievement in various areas. It consists of 10 clusters and 30 subtests that assess a wide range of cognitive abilities and academic skills.
The following table summarizes the clusters, subtests, and cognitive abilities they assess:
| Cluster | Subtests | Cognitive Abilities |
|---|---|---|
| Reading | Letter-Word Identification, Word Attack, Passage Comprehension | Phonological awareness, decoding, vocabulary, comprehension |
| Math | Applied Problems, Computation, Quantitative Concepts | Problem-solving, number sense, measurement, geometry |
| Written Expression | Writing Fluency, Writing Samples | Vocabulary, grammar, sentence structure, organization |
| Oral Expression | Story Retell, Oral Vocabulary | Language comprehension, verbal fluency, storytelling |
| Science | Science Concepts, Science Reasoning | Scientific knowledge, inquiry skills, critical thinking |
| Social Studies | Social Studies Concepts, Social Studies Reasoning | Historical knowledge, geographical knowledge, civic knowledge |
| Study Skills | Map and Graph Interpretation, Reference Skills | Study strategies, information retrieval, problem-solving |
| Technology | Technology Concepts, Technology Applications | Computer literacy, digital literacy, technology skills |
| Fine Arts | Visual Arts, Music | Artistic expression, creativity, musical knowledge |
| Physical Education | Gross Motor Skills, Fine Motor Skills | Motor coordination, physical fitness, dexterity |
2. Cluster Analysis and Interpretation
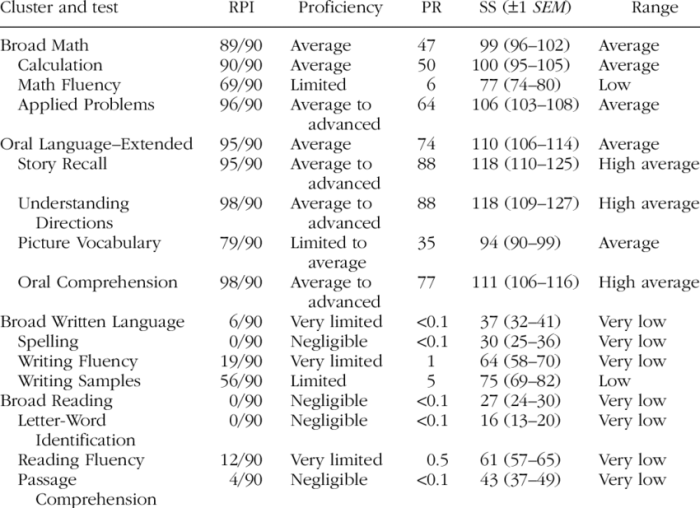
The cluster scores can provide valuable insights into a student’s strengths and weaknesses in academic areas. For example, a student with high scores in the Reading cluster may have strong reading comprehension skills, while a student with low scores in the Math cluster may need additional support in math problem-solving.
By comparing cluster scores, educators can identify areas where students are excelling and areas where they may need additional support. This information can help guide instructional decisions and develop individualized learning plans.
3. Subtest Analysis and Interpretation
The subtest scores can provide even more specific information about a student’s academic skills and knowledge. For example, a student with a high score on the Letter-Word Identification subtest may have strong phonics skills, while a student with a low score on the Oral Vocabulary subtest may need additional vocabulary instruction.
By analyzing subtest scores, educators can pinpoint specific areas where students need additional support. This information can help teachers tailor instruction to meet the individual needs of each student.
4. Comparison with Other Measures
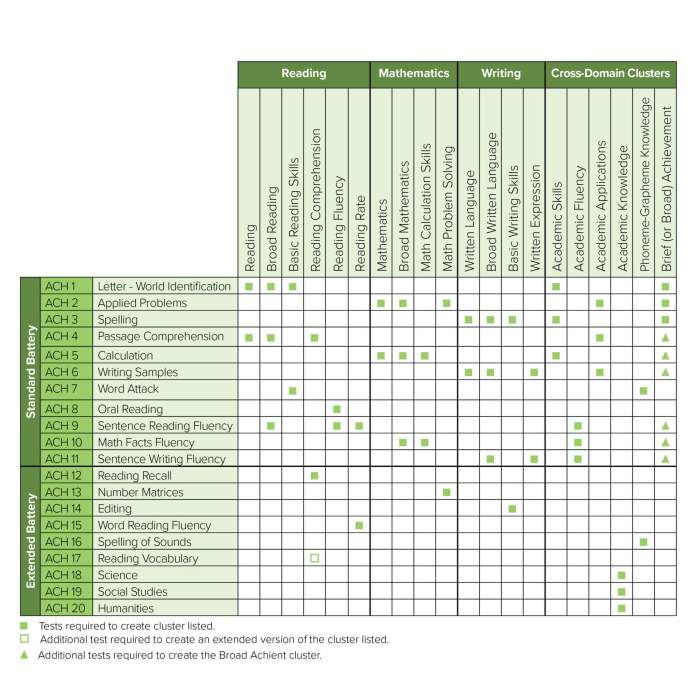
The WJ IV Achievement Clusters and Subtests can be compared to other achievement measures, such as the WISC-V or Stanford Achievement Test, to provide a more comprehensive assessment of a student’s academic skills.
By comparing scores on different measures, educators can gain a better understanding of a student’s strengths and weaknesses across different areas of academic achievement. This information can help educators make more informed decisions about educational interventions and support.
5. Implications for Intervention
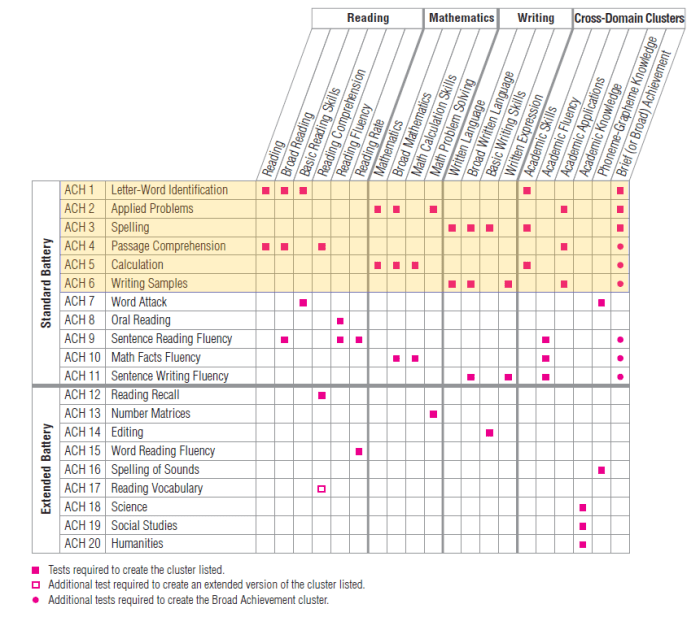
The results of the WJ IV Achievement Clusters and Subtests can be used to develop individualized intervention plans for students who need additional support in specific academic areas.
For example, a student with low scores in the Reading cluster may benefit from intervention focused on improving reading comprehension skills, while a student with low scores on the Math cluster may need intervention focused on developing problem-solving skills.
6. Research and Future Directions
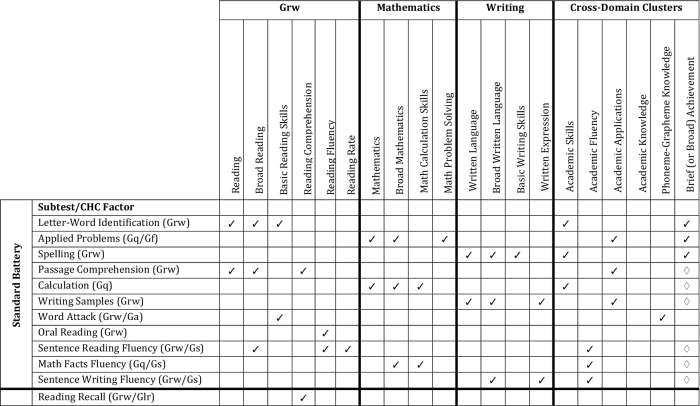
There is a growing body of research on the WJ IV Achievement Clusters and Subtests. This research has helped to validate the assessment and identify its strengths and weaknesses.
Future research directions include investigating the use of the WJ IV Achievement Clusters and Subtests in different populations, such as students with disabilities or students from diverse cultural backgrounds. Additionally, research is needed to explore the relationship between WJ IV scores and other measures of academic achievement and cognitive ability.
FAQ Overview
What are the WJ IV Achievement Clusters?
The WJ IV Achievement Clusters are four broad categories that assess general academic achievement: Reading, Mathematics, Written Language, and Oral Language.
How are the WJ IV Achievement Clusters interpreted?
Cluster scores provide a general overview of a student’s academic strengths and weaknesses. High scores indicate proficiency in the corresponding academic area, while low scores may suggest areas for improvement.
What do the WJ IV Subtests measure?
The WJ IV Subtests assess specific academic skills within each cluster, such as phonemic awareness, reading comprehension, and mathematics problem-solving.