The Triangle Shirtwaist Fire Primary Sources provide a comprehensive and compelling account of the devastating 1911 factory fire that claimed the lives of 146 workers, primarily young immigrant women. Through firsthand accounts, media coverage, and legal documents, these sources shed light on the appalling working conditions, safety violations, and societal failures that contributed to this tragedy.
By examining these primary sources, we gain invaluable insights into the lives of the victims, the heroic efforts of first responders, and the profound impact the fire had on labor rights, fire safety regulations, and urban planning.
Historical Context

The Triangle Shirtwaist Factory was a clothing factory located in the Greenwich Village neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City. It was one of the largest garment factories in the United States at the time, employing over 500 workers, primarily young immigrant women.
The working conditions in the factory were appalling. The workers were forced to work long hours in cramped and unsanitary conditions. The factory was also a firetrap, with only one narrow staircase and no fire escapes. The owners of the factory had repeatedly ignored warnings about the safety hazards in the factory.
Primary Sources
There are a number of primary sources that provide valuable information about the Triangle Shirtwaist Fire. These sources include:
- Eyewitness accounts from survivors and witnesses
- Newspaper articles and photographs
- Official reports from the investigation into the fire
These sources provide a firsthand account of the fire and its aftermath. They help us to understand the conditions that led to the fire, the experiences of the victims, and the public response to the tragedy.
Eyewitness Accounts
Eyewitness accounts provide a vivid and personal account of the Triangle Shirtwaist Fire. These accounts come from survivors, witnesses, and first responders. They describe the chaos and horror of the fire, as well as the bravery and selflessness of those who tried to help.
One of the most famous eyewitness accounts is from Rose Schneiderman, a labor activist who was working in a nearby factory at the time of the fire. She described the scene as follows:
“The girls were jumping out of the windows like flies. They were falling all around me. I saw one girl land on the sidewalk and her head was crushed like an eggshell.”
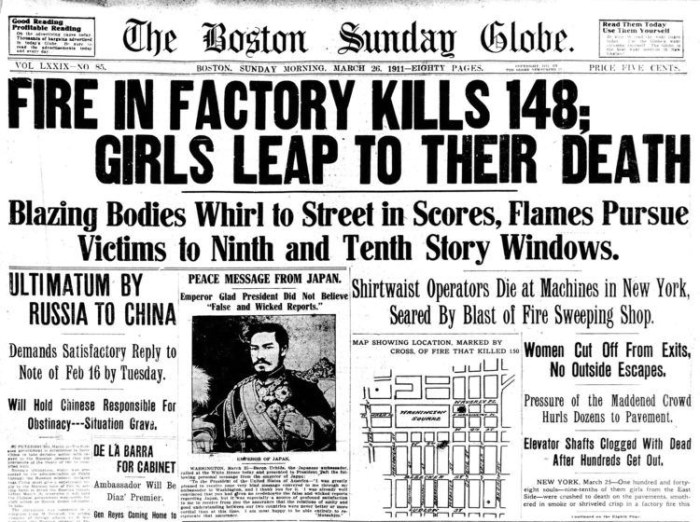
Media Coverage: Triangle Shirtwaist Fire Primary Sources
The Triangle Shirtwaist Fire was widely reported in the media. Newspapers published articles about the fire, and photographs of the victims and the aftermath were circulated around the world. The media coverage of the fire helped to raise public awareness of the dangerous working conditions in factories and led to demands for reforms.
One of the most influential pieces of media coverage was a photograph taken by Lewis Hine. The photograph shows a group of young women jumping from the windows of the burning factory. The photograph became a powerful symbol of the tragedy and helped to galvanize public support for factory safety reforms.
Legal and Regulatory Consequences
The Triangle Shirtwaist Fire led to a number of legal and regulatory changes. In the aftermath of the fire, the New York State Legislature passed a series of laws to improve fire safety in factories. These laws included requirements for fire escapes, sprinklers, and regular inspections.
The fire also led to the creation of the International Ladies’ Garment Workers’ Union (ILGWU). The ILGWU was a labor union that fought for better working conditions and wages for garment workers. The union played a major role in the passage of the Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938, which established a minimum wage and maximum hours for workers.
Cultural and Social Impact

The Triangle Shirtwaist Fire had a profound cultural and social impact. The fire led to a public outcry against the exploitation of workers and the dangerous conditions in factories. The fire also helped to raise awareness of the need for labor unions and for government regulation of industry.
The Triangle Shirtwaist Fire remains a powerful symbol of the struggle for workers’ rights. The fire is commemorated each year with a memorial service at the site of the factory. The fire is also the subject of numerous books, articles, and documentaries.
Expert Answers
What were the main causes of the Triangle Shirtwaist Fire?
The fire was primarily caused by unsafe working conditions, including the presence of highly flammable materials, locked exits, and inadequate fire escapes.
How did the Triangle Shirtwaist Fire impact labor rights?
The tragedy led to widespread public outrage and demands for improved working conditions, resulting in the passage of landmark labor laws and the establishment of the International Ladies’ Garment Workers’ Union.
What are the key primary sources related to the Triangle Shirtwaist Fire?
Important primary sources include eyewitness accounts, newspaper articles, photographs, legal documents, and the report of the New York State Factory Investigating Commission.