Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Concept Map: Embark on an illuminating journey into the intricacies of diabetes mellitus type 2, exploring its pathophysiology, risk factors, diagnosis, management, complications, and preventive measures. This comprehensive resource unravels the complexities of this prevalent condition, empowering you with knowledge and actionable insights.
Unveiling the multifaceted nature of diabetes mellitus type 2, this concept map delves into its pathophysiology, highlighting the interplay of insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion. It illuminates the alarming statistics surrounding its prevalence and incidence, underscoring the urgent need for effective interventions.
1. Definition of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
Diabetes mellitus type 2 (T2DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia resulting from insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency.
Pathophysiology
In T2DM, the body’s cells become resistant to insulin, which is responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. As a result, the pancreas produces more insulin to overcome this resistance. Over time, the pancreas may become unable to produce enough insulin, leading to hyperglycemia.
Prevalence and Incidence
T2DM is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for approximately 90% of all cases worldwide. Its prevalence is increasing rapidly, with an estimated 463 million people living with T2DM in 2019.
Risk Factors and Causes
The exact cause of T2DM is unknown, but several risk factors have been identified, including:
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Family history of diabetes
- Age over 45 years
- Certain ethnicities
2. Symptoms and Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2

Common Symptoms
T2DM often develops gradually, and symptoms may be mild or absent in the early stages. Common symptoms include:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Unexplained weight loss
- Increased hunger
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
Diagnostic Criteria
T2DM is diagnosed based on the following criteria:
- Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥ 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L)
- Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) 2-hour glucose ≥ 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L)
- Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥ 6.5%
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Screening
Early diagnosis and screening are crucial for preventing complications and improving outcomes in T2DM. Regular screening is recommended for individuals at high risk, including those with a family history of diabetes, obesity, or physical inactivity.
3. Management of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2: Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Concept Map

Treatment Options
| Treatment | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|
| Lifestyle modifications | Diet, exercise, weight loss |
| Oral medications | Metformin, sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors |
| Injectable medications | Insulin, GLP-1 agonists |
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications are the cornerstone of T2DM management and include:
- Healthy diet
- Regular physical activity
- Weight loss
- Smoking cessation
Medication
Medications are used to lower blood sugar levels when lifestyle modifications alone are not sufficient. Common medications include:
- Metformin
- Sulfonylureas
- DPP-4 inhibitors
- Insulin
- GLP-1 agonists
4. Complications of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
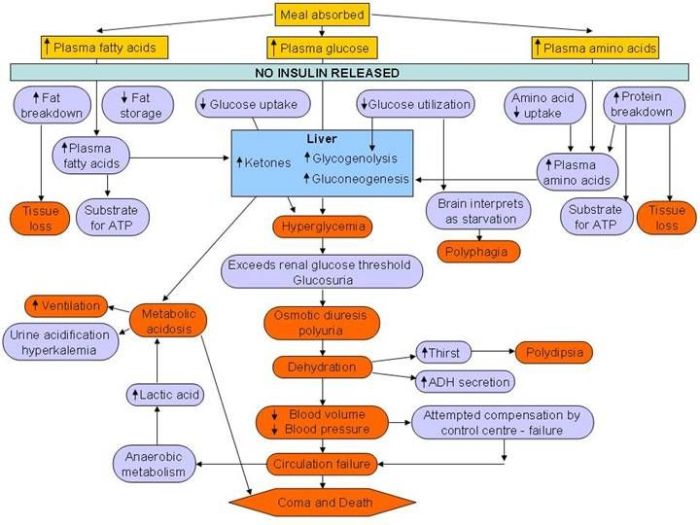
Acute Complications
- Hypoglycemia
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome
Chronic Complications
- Cardiovascular disease
- Stroke
- Nephropathy
- Retinopathy
- Neuropathy
- Foot ulcers
Prevention and Management
Preventing and managing complications involves:
- Optimizing blood sugar control
- Managing blood pressure and cholesterol
- Regular eye and foot exams
- Lifestyle modifications
5. Prevention of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
Modifiable Risk Factors, Diabetes mellitus type 2 concept map
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Unhealthy diet
- Smoking
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
- Age
- Family history
- Race/ethnicity
Evidence-Based Recommendations
Evidence-based recommendations for preventing T2DM include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Adopting a healthy diet
- Quitting smoking
Public Health Campaign
Public health campaigns can raise awareness about T2DM prevention and promote healthy behaviors. Key messages include:
- Know your risk factors
- Make healthy lifestyle choices
- Get regular screenings
User Queries
What is the primary cause of diabetes mellitus type 2?
Insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion are the primary underlying causes of diabetes mellitus type 2.
What are the key risk factors for developing diabetes mellitus type 2?
Modifiable risk factors include obesity, physical inactivity, unhealthy diet, and smoking. Non-modifiable risk factors include age, family history, and certain genetic predispositions.
What are the common symptoms of diabetes mellitus type 2?
Frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, increased hunger, fatigue, and blurred vision are common symptoms of diabetes mellitus type 2.